John Day (carpenter)
John Day (c. 1740 – died 22 June 1774[1]) was an English carpenter and wheelwright. He is the first recorded death in an accident with a submarine.[2] With the financial support of Christopher Blake, an English gambler, Day built a wooden "diving chamber" without an engine. He attached his invention to the deck of a 50-ton sloop named the Maria, which Blake had purchased for £340. The sloop's hold contained 10 tons of ballast, and two 10-ton weights were attached beneath the keel which could be released from inside the diving chamber. An additional 20 tons of ballast would be loaded on the Maria after Day had been locked inside the diving chamber.[2][3][4]
Day had previously spent 6 hours underwater in East Anglia in a different vessel.[5] He bet with Blake that he and his boat could descend to a depth of 130 feet (40 m) and stay underwater for 12 hours.[2][6] Blake lost his initial bets on the venture with other gamblers due to delays in the construction of the diving chamber that prevented Day from making the dive within an initially specified 3-month period.[1]
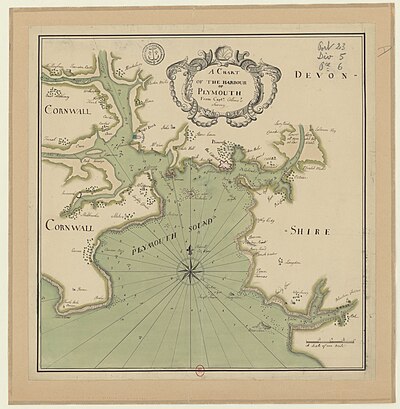
On 22 June 1774,[7] the Maria was towed to a location north of Drake's Island (St. Nicholas' Island) in Plymouth Sound, off Plymouth, England.[4] Day took a candle, water and biscuits on board. The boat was equipped with a hammock for the passenger. After the boat was locked, the weights were loaded and the boat sank forever into the depths. Day had the calculation of the trim completely wrong.[3] It has been speculated that Day may have died from asphyxiation,[1] hypothermia[4] or catastrophic structural failure of the Maria and/or the diving chamber due to water pressure.[2][4][6]
Nikolai Detlef Falck mounted a rescue attempt a month after Day's descent, believing that Day might be alive in a form of suspended animation, but without success. In 1775, Falck published a pamphlet, A philosophical dissertation on the diving vessel projected by Mr Day, and sunk in Plymouth Sound, about Day's experiment.[5] Day's death was the first recorded fatal accident involving a submarine.[3][5]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Chambers, Robert (30 October 1888). "JUNE 22.". The Book of Days: A Miscellany of Popular Antiquities in Connection with the Calendar, Including Anecdote, Biography & History, Curiosities of Literature, and Oddities of Human Life and Character. W. & R. Chambers Publishers. p. 809. Retrieved 7 September 2024 – via Google Books.
- ^ a b c d Churchill, Dennis (2011). "The First Submariner Casualty" (PDF). In Depth (32): 5–6. Archived from the original (PDF) on 23 July 2011. Retrieved 7 June 2011.
- ^ a b c Tall, Jeffrey (2002). Submarines & Deep-Sea Vehicles. Thunder Bay Press. pp. 13–14. ISBN 978-1-57145-778-3.
- ^ a b c d Ecott, Tim (2001). Neutral Buoyancy: Adventures in a Liquid World. New York: Atlantic Monthly Press. pp. 237–240. ISBN 0-87113-794-1. LCCN 2001018840 – via Internet Archive.
- ^ a b c Abel, Stuart (6 June 2020). "The strange tale of the world's first submarine death in Plymouth Sound". Plymouth Sound. The Herald. Plymouth. Retrieved 7 September 2024.
- ^ a b McCartney, Innes (2003). Lost Patrols: Submarine Wrecks of the English Channel. Penzance: Periscope Publishing Ltd. pp. 48–49. ISBN 1-904381-04-9 – via Google Books.
- ^ This date comes from Chambers. According to Churchill and McCartney, Day's fatal dive occurred on 20 June 1774.