Battle of the Saline River
| Battle of the Saline River | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the American Indian Wars | |||||||
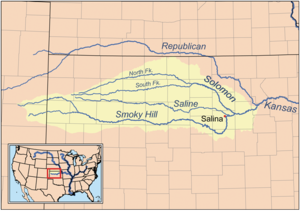
Wounded and lifted on Horse, a painting by C. Taylor from the book Ups and Downs of an Army Office, George Augustus Armes' autobiography. The painting describes when the then Captain Armes was wounded in the hip and lifted up on a horse during the Battle of the Saline River, August 2, 1867. A map of the Smoky Hill River drainage basin in the central Great Plains of North America, State of Kansas, that includes the Saline River. These forks with the Republican River form the Upper Forks of the Kansas River over which several excursions and battles ranged, 1867-1869. | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| Cheyenne | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
William Cody, scout[1] | Tall Wolf (son of Medicine Arrows) | ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
|
| Dog Soldiers | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 34 cavalry[2] | 350-400 warriors or more | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
1 killed several wounded 6 cases of cholera |
6 killed Unknown wounded | ||||||
The Battle of the Saline River in the beginning of August, 1867, was one of the first recorded combats of the Buffalo Soldiers of the U.S. 10th Cavalry. This battle occurred 25 miles northwest of Fort Hays in Kansas on August 2.[3][clarification needed][see discussion]
Prelude
[edit]In the summer of 1867, with realization that the Union Pacific railroad construction in Nebraska would reach Fort Laramie before the Kansas Pacific Railway, and the request of the Denver community for a railroad connection, the route of the Kansas Pacific Railway was diverted from the course of the Republican River to the Smoky Hill River. This was considered a trespass to the Cheyenne and Kiowa claims to Buffalo hunting in western Kansas, who began general raids on the railroad construction and settlers along the new route.[4][5][6][7][8][9]
On August 1,[2] Cheyenne warriors under Tall Wolf, son of Medicine Arrows, attacked and killed a party of railroad workers at Campbell's Camp in eastern modern Ellis County.[10][11] As the narrowly senior officer at the months-old new Fort Hays, then little more than a bivouac, Cpt Henry Clark Corbin [12] dispatched Cpt George Augustus Armes to the camp with Armes' command of 47 troopers of Company F, 10th Cavalry. Cpt. Armes found the slain Campbell's Camp workers in the late afternoon of August 1. Armes attempted an immediate pursuit to the north but soon returned to the camp to request reinforcements.
Battle
[edit]Later in the morning of the 2nd August, without reinforcements and leaving 4 men sick with cholera and some guards and messengers, Armes and 34 troopers followed the active "hostile indian" trail north from Campbell's Camp to the Saline River. Following the Saline River several miles west, the cavalry was surrounded by about 400 horse-mounted Cheyenne warriors. Armes formed a defensive infantry style "hollow square" with the cavalry mounts in the center. Seeking better defensive ground, Armes walked his command south toward Fort Hays while maintaining the defensive square. After 8 hours of combat, 2,000 rounds of defensive fire and 15 miles of movement in the square, the Cheyenne disengaged and withdrew as the troopers gained a bluff in sight of the fort. Company F, without reinforcements, concluded 113 miles of movement during the 30-hour patrol, riding the final 10 miles east back to Fort Hays with only one trooper killed in action. Captain Armes commented later, "It is the greatest wonder in the world that my command escaped being massacred." Armes credited his officers for a "... devotion to duty and coolness under fire."[3][13][2]
Aftermath
[edit]Captain Armes was earnest in locating what he thought was the main Indian village on the Solomon Folks and recovering the large numbers of stolen horse stock he expected to be held there.[14] However, his convalescence kept him unable to ride in the saddle for a couple of weeks. When released from bed rest, his service was limited to riding in his personal carriage up the line to reassure the construction workers. As soon as he could ride, about two weeks later, he led his command to the Solomon Folks in coordination with the 18th Kansas Volunteer Cavalry. Contact with larger numbers of Indians led to the Kansas Battle of Prairie Dog Creek and the (1st) Battle of Beaver Creek. Although casualties were light, the U.S. and Kansas forces withdrew to the railroad for the fall and winter and the seeming U.S. retreat from these battles did not discourage the Cheyenne and Kiowa for the time being.
Even so, the Medicine Lodge Treaty[15] would be signed within a month, but soon broken. It was not until General Sheridan's winter campaign of 1867-68, including the Battle of Washita River, that Indian resistance within the state was broken and the railroad construction secured. Other battles continued after 1868, such as the ones near Sterling, Colorado (the Battle of Summit Springs) and near Cheyenne, Oklahoma, but the fighting in the upper forks of the Kansas River was over.
The last Indian battle in the State of Kansas took place on September 27, 1878. It was known as "Battle of Punished Woman's Fork" or "Battle of Squaw's Den Cave."[11][16]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Colonel W.F. Cody (1920). An autobiography of Buffalo Bill. Cosmopolitan book corporation. p. 100-102. Retrieved 2017-01-27.
- ^ a b c Armes, George Augustus (1900). Ups and Downs of an Army Officer. Washington D. C.: C. L. Taylor Publishing. p. 236-239. Retrieved August 24, 2024.
- ^ a b Wilhelm, Bob (Superintendent of Historic Fort Hays) (2009). "The Battle of the Saline River". Leisure and Sports Review (LASR). Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ Marvin H. Garfield (August 1932). "Defense of the Kansas Frontier 1866-1867". Kansas Historical Quarterly. Kansas Historical Society. Retrieved 2024-08-25.
Overland transportation suffered more than did the frontier settlements during 1866. The Smoky Hill route continued to receive its full share of attention by the Indians. This no doubt was due to the fact that the Union Pacific railroad, eastern division, was moving rapidly westward along the Kaw and Smoky Hill valleys and gave promise of soon threatening the favorite buffalo hunting grounds of the red men. ... Tall Bull, a prominent Cheyenne war chief, [at the Medicine Lodge Council] ably stated the Indians' case when he told the commissioners that the red men were on the warpath to prevent Kansas and Colorado being settled by palefaces. He said that the Indians claimed that part of the country as their own, and did not want railroads built through it to scare away the buffalo.
- ^ Robert Collins (1998). Kansas Pacific An Illustrated History. David City, Nebraska: South Platte Press. pp. 7, 13. ISBN 0-942035-46-1.
... Government support favored the Republican Route. ... Fort Kearny in Nebraska
- ^ Collins. Kansas Pacific. p. 13.
Meanwhile, a survey party was sent west out of Fort Riley. Their charge was to plot the best route to a new destination for the railroad: Denver. By then it was obvious that the UP out of Omaha would win the race for the 100th meridian. UPED President John Perry decided it was advantageous to target a more financially promising destination than Fort Kearny in Nebraska. The standing acts of Congress stipulated that the road should follow the Republican River. A few, however, felt that the Smoky Hill Valley would be a far more direct route to Denver, and construction through the valley would be easier. [Fort Riley/Junction City reached in August] That summer the route was officially changed to follow the Smoky Hill river. The survey party had returned with a plan that would have the road first head for the isolated village of Salina.
- ^ Simon Motz, late citizen of Rome and first Mayor of Hays City (July 7, 1961). Leota Motz (ed.). "Hays Had Its Beginning In 1867 With Founding of Rome". Hays Daily News. Hays, Kansas. p. 27 – via Newspapers.com.
Contracts were awarded during the winter of 1866 and 1867 to build the grade as far west as Park's Fort in [future] Trego county.
- ^ W.A. Hill. "Rome – Predecessor of Hays Founded by "Buffalo Bill" Cody". The William F. Cody Archive. pp. 12–13. Retrieved 2024-08-25.
When the Kansas Pacific was ordered constructed from Ellsworth to Parkfort, near [present day] WaKeeney, the Indians declared it should not be. They murdered six employees of the Kansas Pacific near Victoria. ... Also killed two men at the Butterfield station [Lookout] four miles south of Rome. Also Park and his hired men at Parkfort.
- ^ Collins. Kansas Pacific. p. 13.
[After Fort Hays, it] would then enter the country of three nomadic Indian tribes: the Cheyenne, Arapahoe and Kiowa. ... mile and a half per day. ... Then the Indian raids began.
- ^ Wilhelm, Bob (2009). "The Battle of the Saline River". LASR.
- ^ a b Cozzens, Peter, ed. (2003). Eyewitnesses to the Indian Wars, Volume Three: Conquering the Southern Plains, Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books. ISBN 0-8117-0019-4
- ^ William H. Powell and Edward Shippen (ed.). Officers of the Army and Navy (Regular) Who Served in the Civil War (PDF). p. 101. Retrieved August 24, 2024.
In the mean time he [ Henry Clark Corbin ] had been appointed and confirmed as a captain of the Thirty-eighth Infantry, about to be organized at Jefferson Barracks, Missouri, to which station he immediately repaired, and until May of 1867 he was engaged in its organization. The latter part of May he joined his company at Fort Hays, Kansas. The command was there subjected to the cholera scourge, Colonel Corbin losing twenty per cent of his company by the malady.
- ^ Bob Wilhelm (2009). Kathy Weiser (ed.). "The Battle of the Saline River (1867)". www.Legends of Kansas.com. Retrieved October 28, 2010.
- ^ Armes (1900), p.239. "It is my opinion that a large number of Indians are encamped between the Saline and the Solomon, or on the Solomon, where any amount of stolen stock could be recaptured. provided a sufficient force could go after them."
- ^ "Treaty with the Kiowa and Comanche, 1867" (Medicine Lodge Treaty). Archived November 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine 15 Stats. 581, Oct. 21, 1867. Ratified July 25, 1868; proclaimed Aug. 25, 1868. In Charles J. Kappler, compiler and editor,Indian Affairs: Laws and Treaties — Vol. II: Treaties, pp. 977–982. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1904. Through Oklahoma State University Library, Electronic Publishing Center.
- ^ Hoig, Stan. (1980). The Battle of the Washita: The Sheridan-Custer Indian Campaign of 1867-69. Lincoln, NE: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 0-8032-7204-9. Previously published in 1976 (Garden City, NY: Doubleday). ISBN 0-385-11274-2.
Further reading
[edit]- Greene, Jerome A. (2004). Washita, The Southern Cheyenne and the U.S. Army. Campaigns and Commanders Series, vol. 3. Norman, OK: University of Oklahoma Press. ISBN 0-8061-3551-4.
- Schubert, Frank N. On the Trail of the Buffalo Soldier II: New and Revised Biographies of African Americans (1866–1917), Rowman & Littlefield, 2004. ISBN 978-0-8420-5079-1.
- Tom, Willard, Buffalo Soldiers. Tor/Forge, 1997. ISBN 978-0-8125-5105-1
External links
[edit]- Battle of Punished Woman Fork - Last Indian Battle in Kansas—1878, Keystone Gallery, Scott City, Kansas.
- Legends Of Kansas - History, Tales, and Destinations in the Land of Ahs - Battle of Punished Woman Fork, aka: Battle of Squaw's Den Cave (1878). Legends of Kansas, Warsaw, Missouri.